Geospatial
This page talks about geospatial support in Pinot.
Pinot supports SQL/MM geospatial data and is compliant with the Open Geospatial Consortium’s (OGC) OpenGIS Specifications. This includes:
Geospatial data types, such as point, line and polygon;
Geospatial functions, for querying of spatial properties and relationships.
Geospatial indexing, used for efficient processing of spatial operations
Geospatial data types
Geospatial data types abstract and encapsulate spatial structures such as boundary and dimension. In many respects, spatial data types can be understood simply as shapes. Pinot supports the Well-Known Text (WKT) and Well-Known Binary (WKB) forms of geospatial objects, for example:
POINT (0, 0)LINESTRING (0 0, 1 1, 2 1, 2 2)POLYGON (0 0, 10 0, 10 10, 0 10, 0 0),(1 1, 1 2, 2 2, 2 1, 1 1)MULTIPOINT (0 0, 1 2)MULTILINESTRING ((0 0, 1 1, 1 2), (2 3, 3 2, 5 4))MULTIPOLYGON (((0 0, 4 0, 4 4, 0 4, 0 0), (1 1, 2 1, 2 2, 1 2, 1 1)), ((-1 -1, -1 -2, -2 -2, -2 -1, -1 -1)))GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(POINT(2 0),POLYGON((0 0, 1 0, 1 1, 0 1, 0 0)))
Geometry vs geography
It is common to have data in which the coordinates are geographics or latitude/longitude. Unlike coordinates in Mercator or UTM, geographic coordinates are not Cartesian coordinates.
Geographic coordinates do not represent a linear distance from an origin as plotted on a plane. Rather, these spherical coordinates describe angular coordinates on a globe.
Spherical coordinates specify a point by the angle of rotation from a reference meridian (longitude), and the angle from the equator (latitude).
You can treat geographic coordinates as approximate Cartesian coordinates and continue to do spatial calculations. However, measurements of distance, length and area will be nonsensical. Since spherical coordinates measure angular distance, the units are in degrees.
Pinot supports both geometry and geography types, which can be constructed by the corresponding functions as shown in section. And for the geography types, the measurement functions such as ST_Distance and ST_Area calculate the spherical distance and area on earth respectively.
Geospatial functions
For manipulating geospatial data, Pinot provides a set of functions for analyzing geometric components, determining spatial relationships, and manipulating geometries. In particular, geospatial functions that begin with the ST_ prefix support the SQL/MM specification.
Following geospatial functions are available out of the box in Pinot:
Aggregations
ST_Union(geometry[] g1_array) → Geometry This aggregate function returns a MULTI geometry or NON-MULTI geometry from a set of geometries. it ignores NULL geometries.
Constructors
ST_GeomFromText(String wkt) → Geometry Returns a geometry type object from WKT representation, with the optional spatial system reference.
ST_GeomFromWKB(bytes wkb) → Geometry Returns a geometry type object from WKB representation.
ST_Point(double x, double y) → Point Returns a geometry type point object with the given coordinate values.
ST_Polygon(String wkt) → Polygon Returns a geometry type polygon object from WKT representation.
ST_GeogFromWKB(bytes wkb) → Geography Creates a geography instance from a Well-Known Binary geometry representation (WKB)
ST_GeogFromText(String wkt) → Geography Returns a specified geography value from Well-Known Text representation or extended (WKT).
Measurements
ST_Area(Geometry/Geography g) → double For geometry type, it returns the 2D Euclidean area of a geometry. For geography, returns the area of a polygon or multi-polygon in square meters using a spherical model for Earth.
ST_Distance(Geometry/Geography g1, Geometry/Geography g2) → double For geometry type, returns the 2-dimensional cartesian minimum distance (based on spatial ref) between two geometries in projected units. For geography, returns the great-circle distance in meters between two SphericalGeography points. Note that g1, g2 shall have the same type.
ST_GeometryType(Geometry g) → String Returns the type of the geometry as a string. e.g.:
ST_Linestring,ST_Polygon,ST_MultiPolygonetc.
Outputs
ST_AsBinary(Geometry/Geography g) → bytes Returns the WKB representation of the geometry.
ST_AsText(Geometry/Geography g) → string Returns the WKT representation of the geometry/geography.
Conversion
toSphericalGeography(Geometry g) → Geography Converts a Geometry object to a spherical geography object.
toGeometry(Geography g) → Geometry Converts a spherical geographical object to a Geometry object.
Relationship
ST_Contains(Geometry/Geography, Geometry/Geography) → boolean Returns true if and only if no points of the second geometry/geography lie in the exterior of the first geometry/geography, and at least one point of the interior of the first geometry lies in the interior of the second geometry. Warning: ST_Contains on Geography only give close approximation
ST_Equals(Geometry, Geometry) → boolean Returns true if the given geometries represent the same geometry/geography.
ST_Within(Geometry, Geometry) → boolean Returns true if first geometry is completely inside second geometry.
Geospatial index
Geospatial functions are typically expensive to evaluate, and using geoindex can greatly accelerate the query evaluation. Geoindexing in Pinot is based on Uber’s H3, a hexagon-based hierarchical gridding.
A given geospatial location (longitude, latitude) can map to one hexagon (represented as H3Index). And its neighbors in H3 can be approximated by a ring of hexagons. To quickly identify the distance between any given two geospatial locations, we can convert the two locations in the H3Index, and then check the H3 distance between them. H3 distance is measured as the number of hexagons.
For example, in the diagram below, the red hexagons are within the 1 distance of the central hexagon. The size of the hexagon is determined by the resolution of the indexing. Check this table for the level of resolutions and the corresponding precision (measured in km).
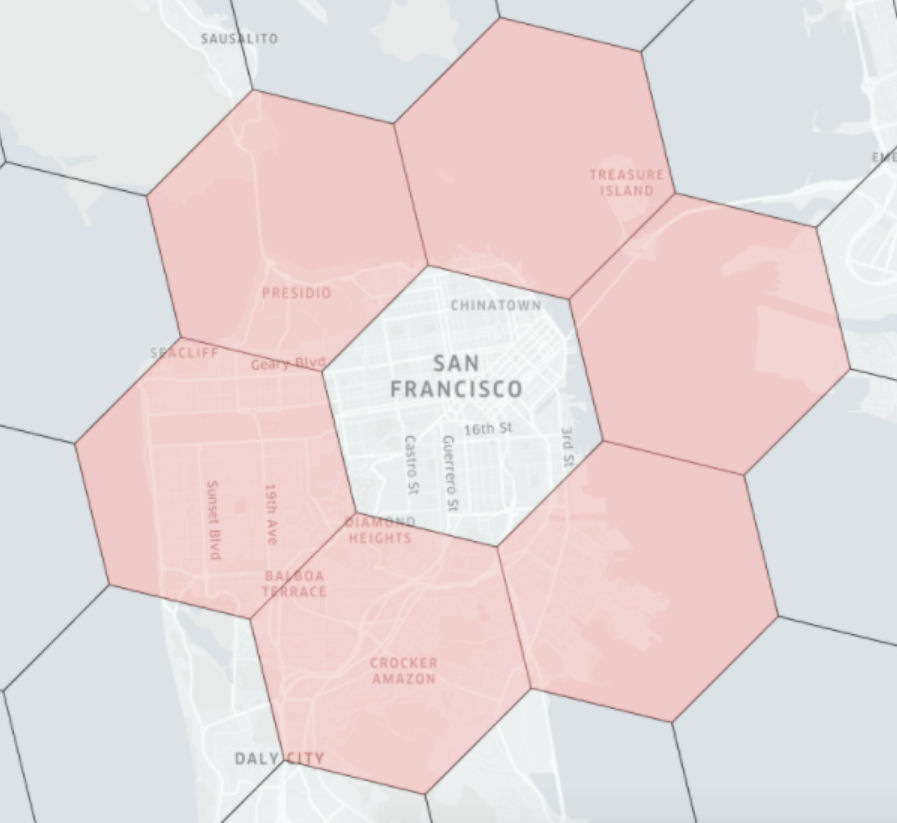
How to use geoindex
To use the geoindex, first declare the geolocation field as bytes in the schema, as in the example of the QuickStart example.
Note the use of transformFunction that converts the created point into SphericalGeography format, which is needed by the ST_Distance function.
Next, declare the geospatial index in the table configuration you need to
Verify the dictionary is disabled (see how to disable the dictionary index).
Enable the H3 index.
It is recommended to do the latter by using the indexes section:
Alternative the older way to configure H3 indexes is still supported:
The query below will use the geoindex to filter the Starbucks stores within 5km of the given point in the bay area.
How geoindex works
The Pinot geoindex accelerates query evaluation while maintaining accuracy. Currently, geoindex supports the ST_Distance function in the WHERE clause.
At the high level, geoindex is used for retrieving the records within the nearby hexagons of the given location, and then use ST_Distance to accurately filter the matched results.
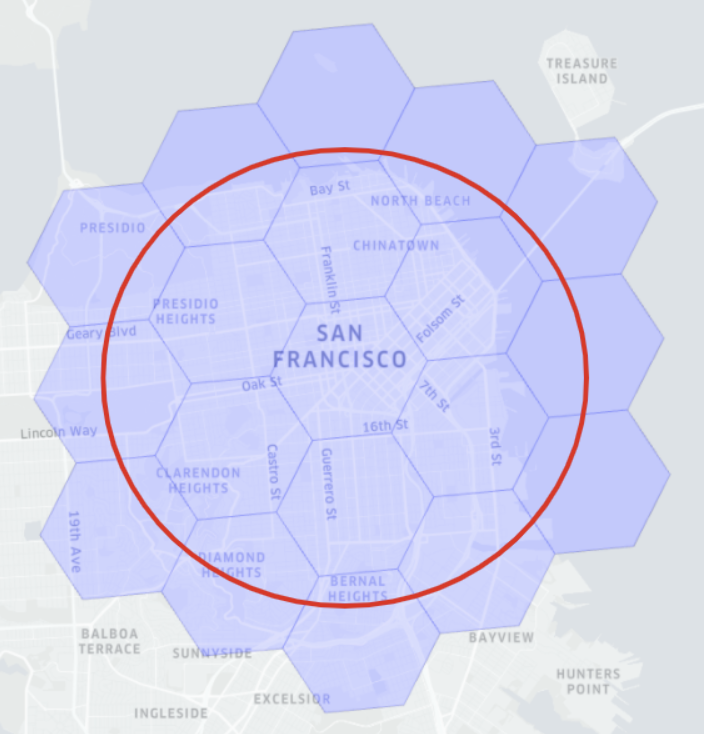
As in the example diagram above, if we want to find all relevant points within a given distance around San Francisco (area within the red circle), then the algorithm with geoindex will:
First find the H3 distance
xthat contains the range (for example, within a red circle).Then, for the points within the H3 distance (those covered by the hexagons completely within
kRing(x)), directly accept those points without filtering.Finally, for the points contained in the hexagons of
kRing(x)at the outer edge of the red circle H3 distance, the algorithm will filter them by evaluating the conditionST_Distance(loc1, loc2) < xto find only those that are within the circle.
Was this helpful?

