Colocated join strategy
Colocated joins is a strategy Pinot can use execute joins without shuffling data between servers when all the following conditions are met:
Both tables are partitioned.
The partition function is the same.
The number of partitions is the same.
The join condition is an equality between the partition columns.
The assignment of partitions to servers is the same.
For each partition, there is a server that has all the segments of the partition for both tables.
As an example, imagine we want to execute the query
SELECT A.col1, B.col2
FROM A
JOIN B
ON A.partitionKeyA = B.partitionKeyBin a scenario where we have tables A and B partitioned by the same function in exactly two partitions and distributed in such a way that:
The 1st partition of A is formed by segments A0-1 and A0-2, stored on servers 1 and 3.
The 2nd partition of A is formed by segments A1-1 and A1-2, stored on server 2.
The 1st partition of B is formed by segment B0-1, stored on server 3.
The 2nd partition of B is formed by segment B1-1, stored on server 2.
In this case, Pinot will try to execute the query in the following way:
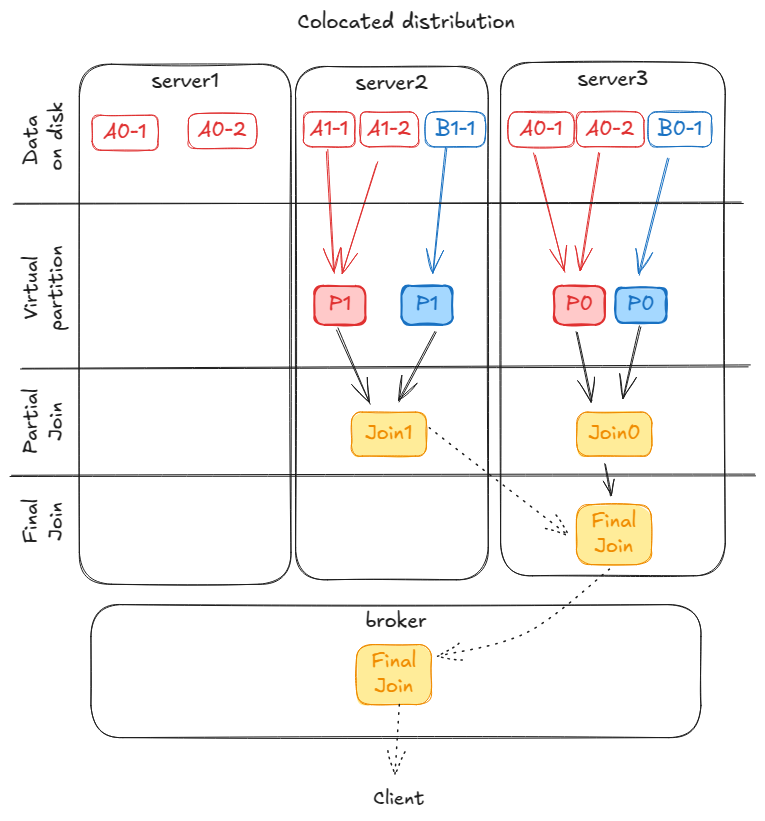
As a side effect, this strategy may not use as many servers as other techniques. For example, the same query using query time partition may use 3 servers, while in this case Pinot can only use server 3 and server 2. Server 1 cannot be used because it does not have all the segments for partition 2 of table B.
How to enable colocated joins
Colocated join optimization is disabled by default in Pinot 1.3.0.
It can be enabled cluster wise by setting the following configuration in the broker:
It can also be enabled/disabled on a per-query basis by setting the following query option:
Even lower level configuration (not recommended)
Colocated joins can also be enabled per-join basis by setting the tableOptions hint directly.
In this case, the partition_function, partition_key, and partition_size are required to be the same for both tables and they must be the same as the ones defined in the table configuration.
This is a very advance and error prone way to configure joins that can also be used to change stage parallelism. Therefore it is recommended.
How to guarantee that colocated joins can be used
As noticed above, in order to use colocated joins, the assignment of partitions to servers must be the same for both tables. Although we can manually assign partitions to servers when creating the tables, they can be moved between servers at any time as a result of a rebalance.
In order to guarantee that colocated joins can be used it is recommended to instruct Pinot to assign the same instances for each partition in both tables. To read more about how to partition a table, see Instance Assignment and Routing.
How to verify colocated joins are being used
As explained, the main advantage when this optimization is enabled is that data doesn't need to be shuffled to execute the join. That can be verified with the rawMessages and inMemoryMessages stats on the mailbox send operator for this stage. All messages should be in memory and rawMessages should be 0 (or not listed at all).
Another way to verify this optimization is being applied is to use the EXPLAIN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN command. You need to use the EXPLAIN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN command. There you will see that MAIL_SEND operators are decorated with [PARTITIONED] and each MAIL_SEND will send the data to another worker in the same server.
Notice that this optimization cannot be seen in the normal EXPLAIN PLAN command.
Was this helpful?

